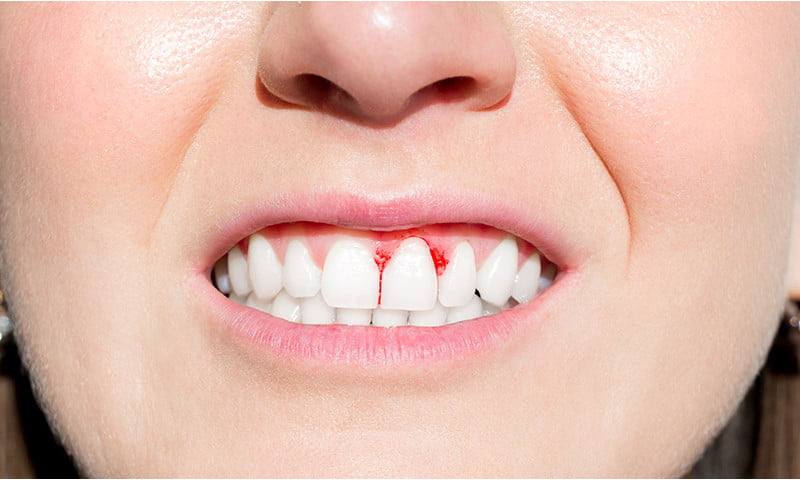
Bleeding gums serve as an initial indicator that requires prompt attention. While it’s common to experience bleeding gums, failing to address them can lead to serious consequences such as gum recession, bone loss, tooth mobility, and eventual gum loss.
Bleeding gums are typically the hallmark symptom of gum or periodontal disease. However, they may also signal other underlying issues like diabetes, hormonal changes, and bruxism, among others. Dental experts at the Concord Dental Practice Center are dedicated to identifying the cause of bleeding gums and providing appropriate treatment, as discussed in this informative blog.
What do bleeding gums indicate?
Bleeding gums are commonly associated with gingivitis and various types of gum disease. However, they can also signal other underlying health issues such as hormonal fluctuations, vitamin deficiencies, blood clotting disorders, and even stress. It is important to recognize bleeding gums as a potential indicator of broader health concerns beyond just oral hygiene.
| Gingivitis is an early form of gum disease characterized by red, swollen, inflamed, and bleeding gums due to the destruction of gum tissues. If left untreated, the condition may aggravate and lead to periodontitis. This is characterized by gum recession, loss of attachment, bone deterioration, mobility, and tooth loss. |
What causes bleeding gums?
There are several reasons why your gums may bleed. These include:
Dental causes
- Poor oral hygiene
- Improper brushing technique (using a hard-bristled toothbrush, or brushing too hard)
- Smoking
- Gingivitis (early-stage)
- Periodontitis (moderate to advanced forms)
- Trench mouth (severe forms of gum disease)
General causes
- Diabetes
- Hormone changes
- Vitamin K deficiency
- Scurvy (a form of vitamin C deficiency)
- Blood thinning medications
- Pernicious anemia
- Hemophilia
- Oral herpes
- HIV
- Leukemia
- Stress
- Dental trauma
How do dentists treat bleeding gums?
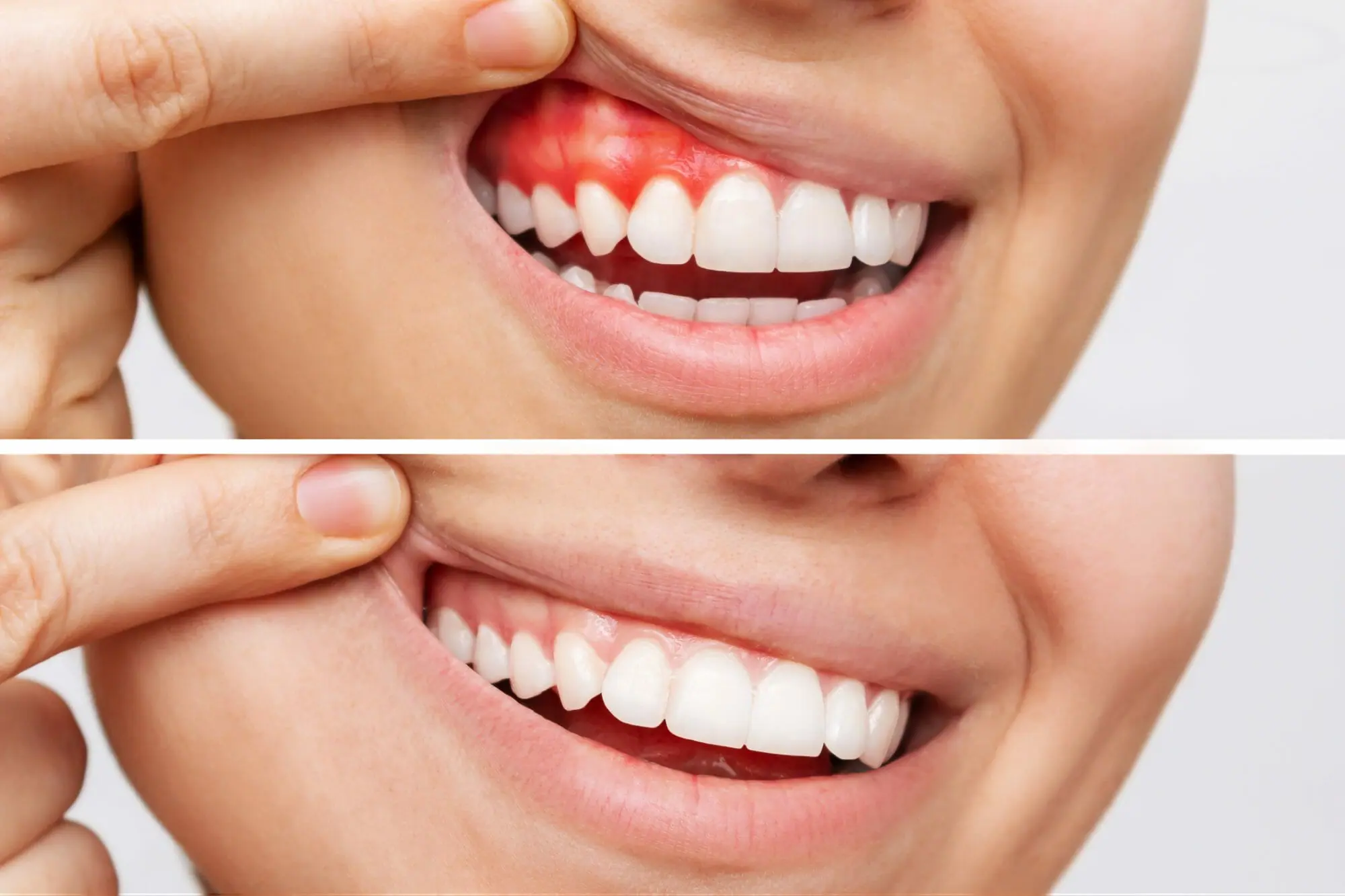
The treatment for bleeding gums depends on the cause. If you experience bleeding gums, consult a dentist or periodontist (gum specialist) for further evaluation
Common gum disease treatments include:
- Improved oral hygiene through regular brushing, flossing, and using antiseptic mouthwash
- Antibiotics
- Scaling and root planing
- Pocket irrigation
- Surgical procedures like gum grafting
- Laser periodontal surgery
Can you prevent bleeding gums?
Yes, you can significantly prevent bleeding gums. Here are a few tips:
- Brush your teeth twice or thrice daily using a soft-bristled toothbrush
- Do not brush aggressively
- Floss once daily
- Rinse your mouth with warm salt water
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash
- Avoid smoking
- Consume a healthy, and well-balanced diet
- Ensure you avoid any forms of dental trauma
Final note
Discovering blood in your sink while brushing is a matter of great concern. While it commonly indicates gum disease, they can signal underlying health issues. If you observe bleeding gums, it is advisable to consult a dentist and discuss the frequency and severity of the bleeding. Your dentist will diagnose the exact cause of bleeding and suggest a suitable treatment plan to help restore your oral health.